Home / Knowledge Hub / FAQ
FAQ
Particle Analytical – Frequently Asked Questions
From GMP and Hauser ratio to sample submission. And more.
Particle Analytical is aimed to provide you with valuable information. Whether you have questions about a Quality approach, Scientific definitions or simply need practical information, e.g. for the sample delivery – take a second to browse through the FAQ section.
How do I submit a sample?
In order to secure a smooth sample registration process, please fill the Sample Submission Form and add it to the sample delivery. Besides the necessary sample information, we need to get the Material Safety Data Sheet for the Material in order to evaluate the safety for the lab technicians. For any questions rearding your sample delivery, please feel free to get in touch.
How do I get a quote?
If you are interested in getting a quote, please fill in our quote form, and we will get back to you with a concrete quote for your request. It’s free to get a quote.
If you are not yet ready for getting a quote, give us a call or send us an email, so we can help you finding the best way forward.
Where can I find the GMP certificate of Particle Analytical?
We are proud of our GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) certification. If you are interested in seeing our certificate, for all EU-European companies, you can find GMP certficates in the database EudraGMDP, where it’s free to download.
How do you get GMP certified in Europe?
To obtain Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) certification in Europe, pharmaceutical manufacturers must adhere to the guidelines outlined in the EU GMP regulations.
EU GMP regulations are a set of standards that ensure the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products throughout the manufacturing process. They cover various aspects such as facilities, equipment, personnel, documentation, and quality control. In Danmark, the Danish Medicines Agency is responsible for the issuance of GMP certificates to pharmaceutical manufacturers and API manufacturers.
Why is a method validation necessary?
It is GMP requirement to have method validated before product release.
Is it sufficient to have one method for all products?
It recommended to have a method for each product.
What are the regulatory requirements to determine particle size?
In the ICH guidelines, several references to determination of particle sizes are found (e.g. ICH Q6A, Q8 & Q9). Please visit our section on ICH guidelines to get more insight.
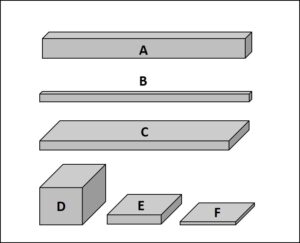
How are particle shapes defined?
Based on European Pharmacopeia (2.9.37), particles can be described as
A. Columnar
B. Acicular
C. Lath
D. Equant
E. Plate
F. Flake
What is the European pharmacopoeia?
The European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) is a legally binding collection of quality standards for medicines used in Europe. Every 3 years it is updated by the European Pharmacopoeia Commission.
The European Pharmacopoeia covers the quality and purity requirements for active substances, excipients, and medicinal products, as well as analytical methods for their testing. Pharmaceutical manufacturers, regulatory authorities, and laboratories across Europe, reference the European Pharmacopoeia to ensure compliance with quality standards.
Do you have a Quality System?
Yes, Particle Analytical is following the guidelines according to European Pharmacopeia. We are GMP certified and FDA approved.
How does Particle Analytical handle Out of Specification (OOS)?
If a result is out of of specification (OOS), we are from a legally perspective obliged to investigate internally. The purpose of the internal investigation is to find the root cause – was it an laboratory error or was it maybe the sample condition who lead to rsult out of specification?
If an OOS occurs, the Particle Analytical team follows the following procedure:
Quality Control informs the customer
- QC opens an internal OOS investigation
- QC & the responsible technical specialist do lab investigation
- QA finally approved the OOS report
- Customer received per e-mail as pdf the OOS report and the Certificate of Analysis
- Customer decides, if a reanalysis shall be carried out
The customer will receice the Certificate of Analyses and the outcome of the OOS as pdf by E-Mail. Any additional anaylses on the OOS – sample is an individual customer decision.
Can I have a customer audit?
Yes, customer can choose if they prefer a remote audit or an On-Site – Audit. As an audit is requires additional QA ressources, laboratory and QC time we will charge the customer for an Audit.
What is the Hausner ratio?
The Hausner Ratio is a measure used in the field of powder technology to assess the flowability of a powder. It is defined as the ratio of the tapped density to the bulk density of the powder. Here’s how it is calculated and what it indicates:
Bulk Density:The mass of the powder divided by its volume, measured without any compaction.
Tapped Density:The mass of the powder divided by its volume after it has been tapped or compacted to reduce the volume.
Interpretation:
- Ratio < 1.25: Indicates good flowability
- Ratio 1.25 – 1.4: Indicates moderate flowability
- Ratio > 1.4: Indicates poor flowability, suggesting that the powder may be cohesive and difficult to handle.
What is the Carr's index?
Carr’s compressibility index can be used as an indirect measurement of the flow properties of powder.
Bulk density affects the value of the compressibility index, and factors such as particle size and shape, surface area and moisture content can influence its value.
- Interpretation:
A low value < 15 is an indication of free-floating powder - A high value above 32 is an indication of a poorly floating powder
What is the Mie model
For smaller particles, it is appropriate to use Mie Theory. The Mie model takes into account both diffraction and diffusion of the light around the particle in its medium. To use the Mie model, it is necessary to know the complex refractive index of both the sample and the medium.
The Fraunhofer theory is applicable for large particles compared to the wavelength l (diffusion and absorption are not considered). This complex index has a real part, which is the standard refractive index, and an imaginary part, which represents absorption:
- Complex index = m
- m = a + b
- a: real part
- b: imaginary part
How does Air Permeability operate?
The process of Air Permeability testing unfolds through meticulous steps:
- Sample preparation:
Samples are carefully dried and compressed to create a uniform powder bed, eliminating variables that could impact the air flow measurement. - Air flow measurement:
Air is gently passed through the compressed powder bed. The rate at which air can move through the material is meticulously recorded, as it’s directly influenced by the texture and structure of the material’s outer surface. - Surface area calculation:
Utilizing the collected air flow data, the specific surface area is calculated. This is achieved by correlating the air flow rate to the surface area accessible to air, emphasizing the material’s outer surface characteristics. - Result analysis:
The calculated surface area provides a quantitative measure of the material’s outer surface, aiding in material characterization and quality assurance practices.
Please pick a subject
Knowledge Hub
Explore our Knowledge Hub for regulatory guidelines, publications, events and FAQ, that bring you insights into particle analysis
How we can help
Learn more about How we can help you addressing problems in your development or manufacturing process, by applying our strong technical and analytical skills.
Why choose us
By choosing Particle Analytical, you get a strong and specialized partner, with a wide range of analysis, scalable and flexible services, and strong accreditations.