FTIR
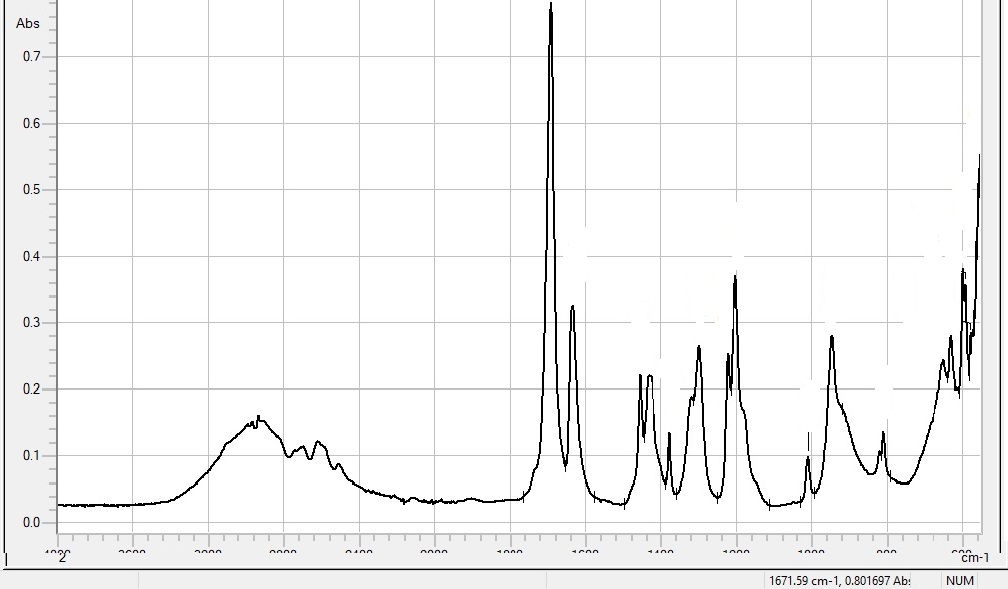
In Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), infrared radiation is passed through a sample. The resulting spectrum represents the molecular absorption, creating a molecular fingerprint of the sample.
- Identification of API as a routine analysis
- Identification of impurities
- Quantification of components in mixtures, for instance determination of content of amorphous material in a crystalline sample (percent crystallinity).
- Examination of changes in the solid state due to interactions with excipients – i.e. compatibility studies in order to chose the most stable excipients for the final product.
- Identify polymorphic form and verify salt formation
For Material Experts:
Instrument and measuring principles, FTIR
When a material is irradiated with infrared radiation, absorbed I.R. radiation excites molecules into a higher vibrational state. The wavelength of light absorbed by a particular molecule is a function of the energy difference between the at-rest and excited vibrational states. The wavelengths that are absorbed by the sample are characteristic of its molecular structure.
The region from 1500 – 400 wavenumbers is referred to as the fingerprint region. Absorption bands in this region are generally due to intramolecular phenomena and are highly specific to each material. The specificity of these bands allows computerised data searches within reference libraries to identify a material, including I.D. of impurities. FTIR is also used for quantification of components in mixtures, for instance, determination of the content of amorph material in a crystalline API, as the absorbance is proportional to the content of the given component. I.e. using FTIR, the percent crystallinity of a sample can be determined.
| Instrument | Shimadzu IRTracer-100 FTIR with SPECAC Golden Gate ATR unit |
| USP/Ph. Eur. | Ph. Eur. 2.2.24 Absorption spectroscopy infrared USP ˂197˃ Spectrophotometric identification test |
| Sample amount | 1-5 mg |
| Temperature | Ambient |
| Result | FTIR generates absorption or transmission spectra as a function of wavenumbers. Measuring range: 4000-500 cm-1 |



